Pumps
- Product List
- The Technology
GNH Series
Displacement:
24.5 ml/rev (G35)
Differential Pressure (max):
6.9 bar | 100 psi
System Pressure (max):
103 bar | 1500 psi
GMH Series
Displacement:
12.2 ml/rev (G25)
Differential Pressure (max):
8.7 bar | 125 psi
System Pressure (max):
103 bar | 1500 psi
GA Series
Displacement:
0.017 ml/rev (X21)
0.042 ml/rev (V21)
0.092 ml/rev (T23)
Differential Pressure (max):
5.2 bar | 75 psi
System Pressure (max):
21 bar | 300 psi
GAH Series
Displacement:
0.017 ml/rev (X21)
0.042 ml/rev (V21)
0.092 ml/rev (T23)
Differential Pressure (max):
5.2 bar | 75 psi
System Pressure (max):
345 bar | 5000 psi
GB Series
Displacement:
0.26 ml/rev (P23)
0.58 ml/rev (P25)
1.17 ml/rev (P35)
Differential Pressure (max):
8.6 bar | 125 psi
System Pressure (max):
21 bar | 300 psi
GC Series
Displacement:
0.811 ml/rev (M23)
1.82 ml/rev (M25)
3.48 ml/rev (M35)
Differential Pressure (max):
8.6 bar | 125 psi
System Pressure (max):
103 bar | 1500 psi
GD Series
Displacement:
3.48 ml/rev (M35)
Differential Pressure (max):
6.9 bar | 100 psi
System Pressure (max):
103 bar | 1500 psi
GJ Series
Displacement:
0.316 ml/rev (N21)
0.64 ml/rev (N23)
0.91 ml/rev (N25)
1.23 ml/rev (N27)
Differential Pressure (max):
5.5 bar | 80 psi
System Pressure (max):
21 bar | 300 psi
CA Series
Recommended Max Speed:
6,000 RPM
System Pressure (max):
14 bar | 200 psi
GAF Series
Displacement:
0.092 ml/rev (T23)
Differential Pressure (max):
17.2 bar | 250 psi
System Pressure (max):
21 bar | 300 psi
GJR Series
Displacement:
0.316 ml/rev (N21)
0.64 ml/rev (N23)
1.23 ml/rev (N27)
Differential Pressure (max):
5.5 bar | 80 psi
System Pressure (max):
21 bar | 300 psi
GLH Series
Displacement:
4.6 ml/rev (H21)
6.2 ml/rev (H23)
7.7 ml/rev (H25)
Differential Pressure (max):
8.6 bar | 125 psi
System Pressure (max):
103 bar | 1500 psi
External Gear - Cavity Style
Cavity style gear pumps consists of two or more rotating gears which interlock together. One of the gears is turned by a power source and drives the other gear(s). The spaces between the gear teeth carry the fluid from the inlet to the outlet. The gear interlace point prevents the fluid from returning to the inlet.

External Gear - Suction Shoe Style
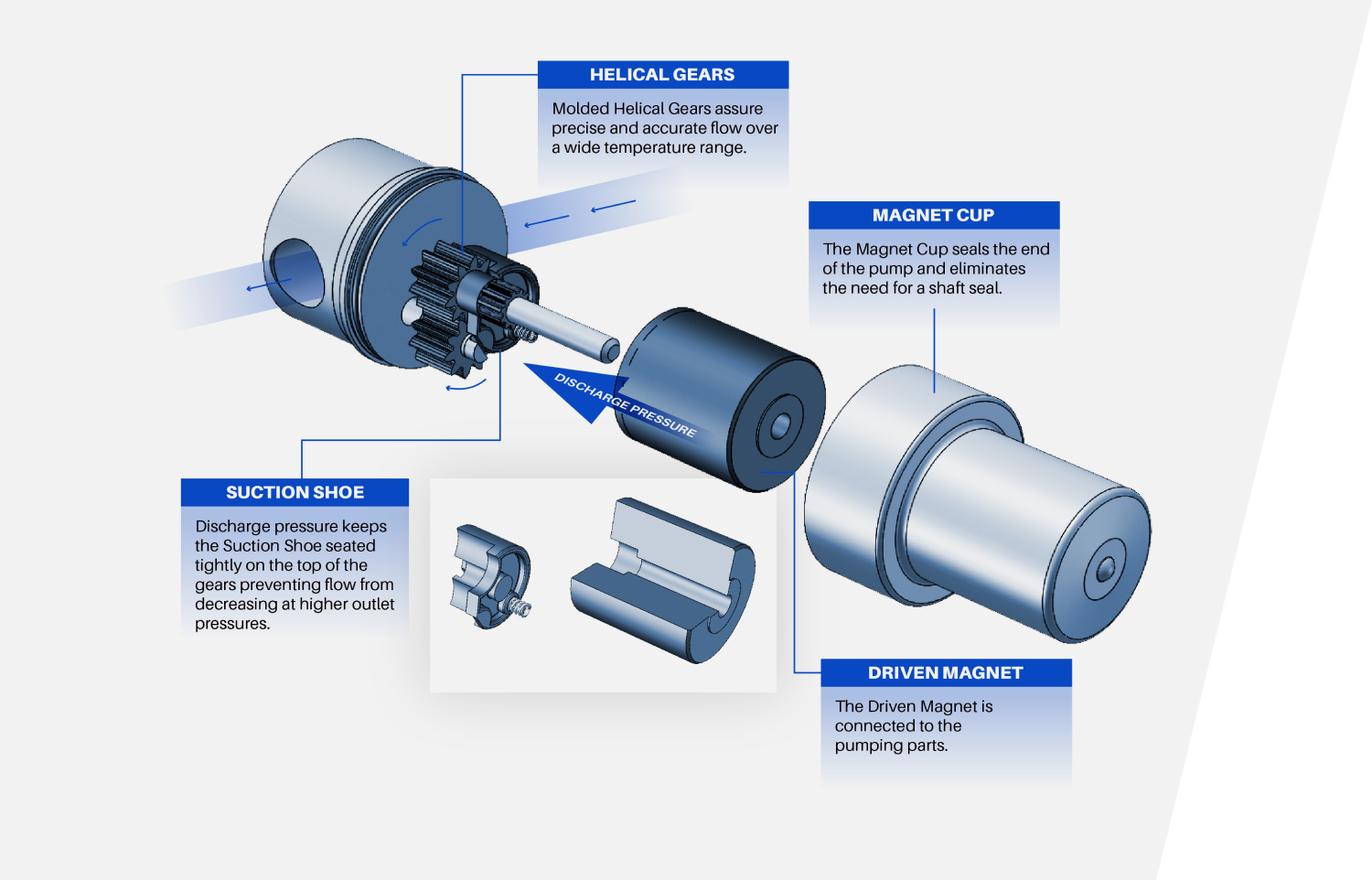
Our trademark, patented suction shoe pressure-loaded gear pump design features a “suction shoe” that allows the pump to self-compensate for wear. Suction shoe pumps maintain high-volumetric efficiency, even at elevated pressures. Additional benefits include near-zero slip for accurate metering, long life, and more stable performance as pump components wear or thermally expand. The suction shoe pump, unlike any other gear pump on the market, self adjusts on the job for reliable, pulseless flow, and features easier maintenance with less downtime than standard pumps.
Centrifugal
Centrifugal pumps offer a reliable, simple, long-lasting design for higher flow applications. Using the unique magnetic drive technology, centrifugal pumps provide excellent chemical resistance and energy-efficient fluid delivery. Integrated impeller and magnet assemblies reduce the number of rotating parts to maximize pump life.
Centrifugal pumps consist of an impeller rotating within a casing. Liquid directed into the center of the rotating impeller is picked up by the impeller vanes and accelerated to a high velocity. When the liquid in the impeller is forced away from the center of the impeller, a reduced pressure is produced and consequently more liquid flows forward. There is no closed volume, as in a positive displacement pump, therefore producing a steady flow through the impeller. The pump basically increases the Bernoulli head of the flow between the eye and the exit of the pump.

Pumps Technology Summary
Advantages & Limitations
External Gear Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps
Maximum Flow Rate
42 L/min (11.1 gpm) (higher possible)
27 L/min (7.1 gpm)
Volume Displacement per Revolution
.017 ml
3 ml
Drive Speed rpm (maximum)
6000
10000
Maximum Differential Pressure
8.6 bar (125 psi) (higher possible)
~14 meters head (~46 ft head)
Accuracy and Repeatability
high
n/a
Autoclavability / Sterility
not with PTFE gears
not with PTFE components
Calibration / Recalibration
frequent
low frequency
Chemical Inertness
high
high
Corrosion Resistance
good
good
Cross-Contamination
yes (thorough flushing is required)
yes (thorough flushing is required)
Dead Volume
very low
low
Direct Contact with Mechanical Parts of the Pumphead
yes
yes
Run Dry
no
no
Fittings
hose barb or screw coupling
hose barb or screw coupling
Flow Rate Sensitivity to Differential Pressure
low
very high
Interchangeability of Pumpheads
easy
easy
Leakage Susceptibility
low
low
Maintenance (Time and Cost)
medium (service kits)
medium (service kits)
Multi-Channel Systems
no
no
Pulsation Ratio
very low
n/a
Pumping of High Viscosity Liquids
yes
no
Pumping of Suspensions, Sludges and Particles
yes
yes
Self-Priming
yes
no
Shearing Forces
moderate
low
Siphoning Effect When Pump Is Stopped
yes
yes
Suction Lift
dry: ~1.52 m (5 ft)
wet: ~3.96 m (13 ft)
n/a
Find a Distributor
Get a Quote
Find a Product
Headquarters
Micropump Inc.
1402 NE 136th Avenue
Vancouver, WA 98684-0818 USA















